 Based on his interpretation of ancient sources, Immanuel Velikovsky argued famously that Venus had emerged from Jupiter as a comet; interacted with the Earth and Mars in the second and first millennia BC, causing the Bronze Age catastrophes; and then finally settled into a nearly circular orbit of the Sun.
Based on his interpretation of ancient sources, Immanuel Velikovsky argued famously that Venus had emerged from Jupiter as a comet; interacted with the Earth and Mars in the second and first millennia BC, causing the Bronze Age catastrophes; and then finally settled into a nearly circular orbit of the Sun.
Three lines of reasoning support a Revised Venus Theory.
First, instead of the various unpersuasive suggestions that Velikovsky and others have made for how a cometary Venus could have emerged from Jupiter, we should consider the possible consequences of the immense gravitational field of Jupiter, which pulls toward it a stream of asteroids and comets, as with Shoemaker-Levy 9 in 1994.
Tags: Abu Simbel, Athena, Black Drop, Great Serpent Mound, Jupiter, Mars, Metis, Nefertari, planetary science, Poseidon, Ramses II, tidal locking, Velikovsky, venus, Zeus
 Once a leading theory of the origin of the Earth-Moon system, the Capture Theory is simple and intuitively plausible. The numerous instances of moons with retrograde orbits show that capture is fairly common. The lunar orbit’s three moments of inertia are consistent with a past very eccentric orbit, suggestive of capture. However, the Moon would, it was thought, have to come from a different part of the solar system to account for its very depleted iron compared to the Earth’s iron, which means that it would approach the Earth at a high velocity that would prevent capture. Researchers have searched in vain for a braking mechanism that would slow it down so it could be captured. Still, the accumulated evidence and arguments make the Capture Theory a viable one.
Once a leading theory of the origin of the Earth-Moon system, the Capture Theory is simple and intuitively plausible. The numerous instances of moons with retrograde orbits show that capture is fairly common. The lunar orbit’s three moments of inertia are consistent with a past very eccentric orbit, suggestive of capture. However, the Moon would, it was thought, have to come from a different part of the solar system to account for its very depleted iron compared to the Earth’s iron, which means that it would approach the Earth at a high velocity that would prevent capture. Researchers have searched in vain for a braking mechanism that would slow it down so it could be captured. Still, the accumulated evidence and arguments make the Capture Theory a viable one.
But
Tags: Capture theory, Earth, earth science, Earth-Moon system, Giant Impact, Jupiter, Mars, Mercury, moon, origin of Earth, origin of Mars, origin of the Moon, Outer Solar System Origin of the Terrestrial Planets, oxygen isotope ratios, planetary science
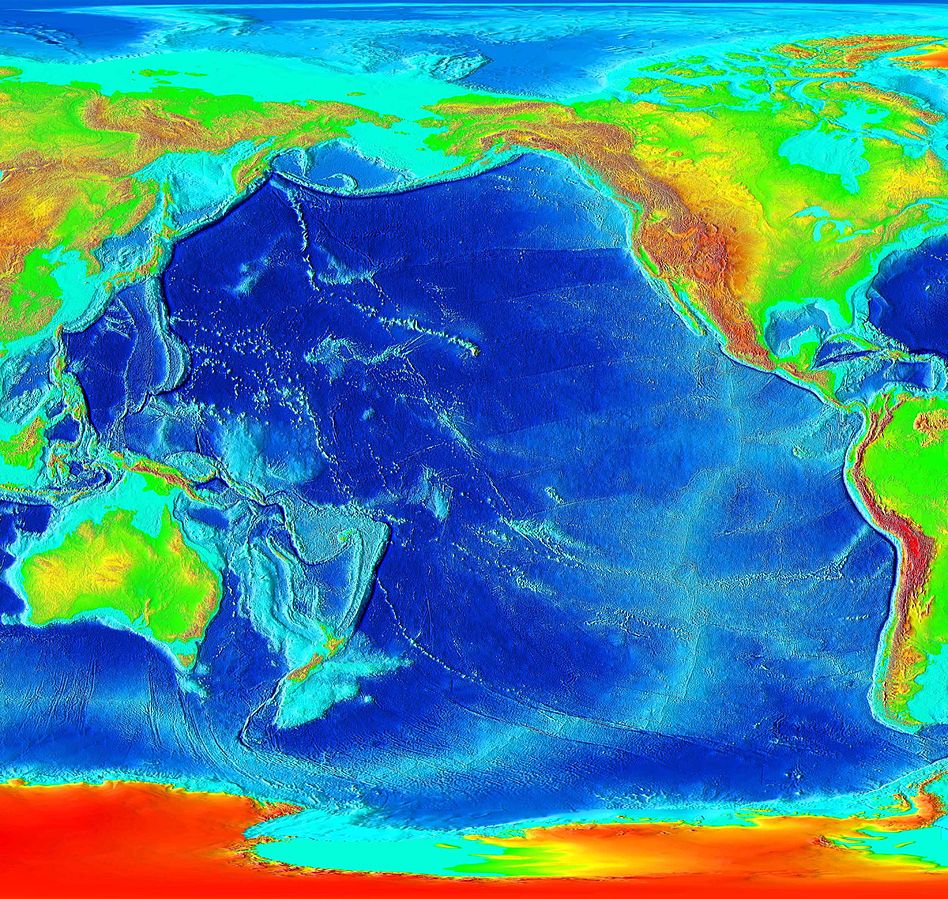
There are good reasons to think that Earth and Mars originally formed a single planet outside the orbit of Jupiter. Early in Solar System history, Jupiter’s powerful gravitational field pulled this planet past the gas giant. As the planet neared Jupiter, tidal friction heated it to the melting point, and Jupiter tore Mars away from Earth, leaving the Pacific Basin and an array of evidence on both planets. Earth and Mars then sped off into the inner solar system.
originally formed a single planet outside the orbit of Jupiter. Early in Solar System history, Jupiter’s powerful gravitational field pulled this planet past the gas giant. As the planet neared Jupiter, tidal friction heated it to the melting point, and Jupiter tore Mars away from Earth, leaving the Pacific Basin and an array of evidence on both planets. Earth and Mars then sped off into the inner solar system.
How Do We Know This?
Tags: Earth, earth science, geomagnetism, Hawaiian Islands, hotspots, Mars, moon, Pacific, planetary science, plate tectonics, plumes, seismography, volcanism


When Venus first appeared in the skies around 2525 BC, ancient peoples worldwide strove to come to terms with this brilliant and awesome new comet-planet (the best account is in Immanuel Velikovsky, Worlds in Collision, though it has been corrected in a Revised Venus Theory). That meant assigning the deity a gender and a name.
In the Near East, they tried both genders. In its masculine incarnation, Venus became the Bull of Heaven (as Velikovsky pointed out, the comet-planet’s body blocked the sun’s rays from the central portion of its tail and thus it was seen as having two horns). In its feminine version, Venus was called Ishtar or Astarte; and in the Levant Astarte was depicted with serpents in her hands—the twin tails of the comet.
In Greece, according to Velikovsky, planet Venus was originally named Athena.
Tags: ancient history, Athena, Bull of Heaven, crete, etymology, Gilgamesh, Greece, Jupiter, Linear B, Master Impression, minoan, Minotaur, Mycenaean, mythology, Phoenicia, planetary science, Poseidon, science, Snake Goddess, Velikovsky, venus
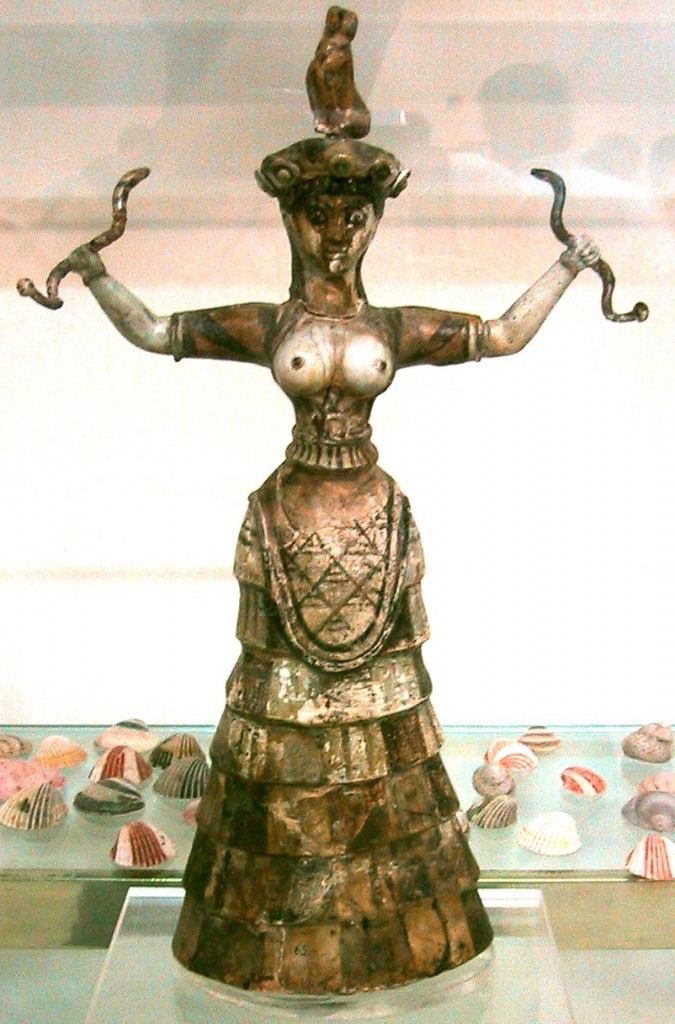 The famous Snake Goddess of ancient Crete has long attracted students of history and art. Elegant, risquée, enigmatic, she embodies the mystery and allure of Minoan civilization.
The famous Snake Goddess of ancient Crete has long attracted students of history and art. Elegant, risquée, enigmatic, she embodies the mystery and allure of Minoan civilization.
Tags: Ancient Greece, Ancient Near East, art, Astarte, crete, iconography, Ishtar, isis, minoan, Minoan snake goddess, planetary science, Velikovsky, venus
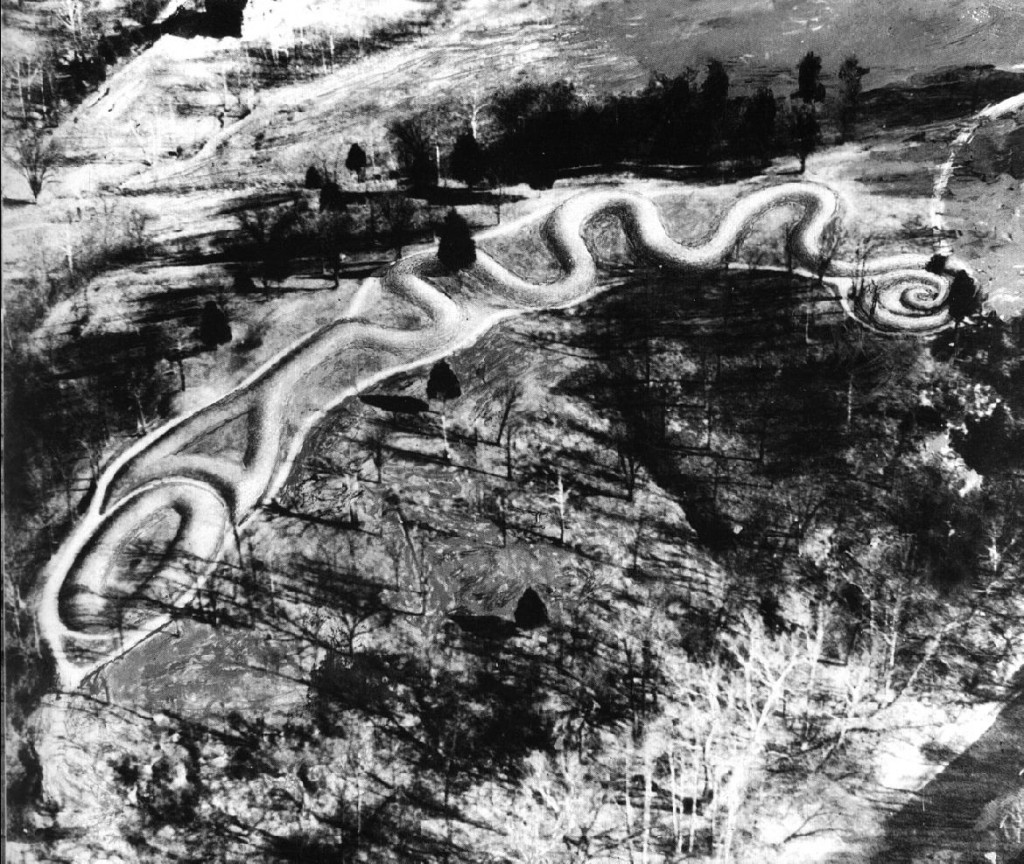

411-meter long Great Serpent Mound in Ohio is the world’s longest effigy monument. Archaeological investigations have yielded conflicting results about its initial construction date, and various theories regarding its meaning have failed to gain traction. But a Revised Venus Theory–one that modifies Immanuel Velikovsky’s theory that the planet Venus was originally a comet that approached the Earth and caused great devastation–neatly matches key characteristics of the Great Serpent Mound.
Recently, this Revised Venus Theory has gained additional credibility from a commonsensical explanation of how a comet-like Venus could have seemed to emerge from Jupiter as in ancient Hindu and Greek myths (Jupiter’s gravity pulled it from the outer solar system), including a simple, obvious reinterpretation of the Metis myth. Much new evidence has also emerged. And the theory has found powerful substantiation from a reinterpretation of the headdress of Queen Nefertari of Egypt, consort of Pharaoh Ramses II, in this image from Abu Simbel (Ramses II’s headdress appears to contain Mars with two moons and a tail, either borrowed from Venus in an encounter or from Martian dust stirred up by an encounter).
Tags: Ancient Egypt, Ancient North America, catastrophe, comet, iconography, planetary science, serpent mound, Velikovsky, venus

Decades of meticulous investigation have revealed many features of the 1st Century BC Antikythera Mechanism, a portable planetarium that demonstrated the motion of celestial objects. But we must question researchers’ conclusion that the Mechanism incorrectly represented the orbit of Mars, in particular, by roughly 30 degrees during retrograde motion.
This discrepancy seems anomalous in a sophisticated device that otherwise exhibited a much smaller range of error. So maybe there is some other explanation.
Tags: ancient astronomy, Antikythera Mechanism, Bronze Age catastrophes, Immanuel Velikovsky, Jupiter, Mars, planetary science, Revised Venus Theory, venus
 If we can interpret certain ancient myths correctly, they could lead us to more accurate and penetrating views of the history of the Earth and the solar system. They might teach us about the forces at work and explain anomalies bequeathed to us by a long-hidden past. But how can we interpret these myths, the products of minds so far removed from ours? How do we know which interpretation is correct, if any? Are we doomed to speculate without ever achieving certainty?
If we can interpret certain ancient myths correctly, they could lead us to more accurate and penetrating views of the history of the Earth and the solar system. They might teach us about the forces at work and explain anomalies bequeathed to us by a long-hidden past. But how can we interpret these myths, the products of minds so far removed from ours? How do we know which interpretation is correct, if any? Are we doomed to speculate without ever achieving certainty?
Here we will interpret two Bronze Age myths to illustrate the high scientific value such myths might contain. We will also see how easy it can be to understand a myth once the right interpretation becomes available.
Tags: Ancient China, Ancient Greece, Bronze Age catastrophes, comets, earth science, history of solar system, interpretation of myths, Jupiter, myths, philosophy of science, planetary science, Velikovsky, venus, Zeus
 New evidence and interpretation at the intersection of planetary science and religion can help us better understand the history of the Ancient Near East and of the origins of Islam.
New evidence and interpretation at the intersection of planetary science and religion can help us better understand the history of the Ancient Near East and of the origins of Islam.
A Revised Venus Theory corrects Immanuel Velikovsky’s original theory that the planet Venus first entered the inner solar system as a comet with a bifurcated tail around 1500 BC (new evidence indicates around 2525 BC). Now we have a much better explanation of the origin of Venus (rather than fissioning off of Jupiter, it was pulled from the outer solar system by Jupiter’s gravity and, via tidal heating, became a comet with a long tail). Venus interacted with the Earth on a 52-year cycle during the Late Bronze Age, causing catastrophes worldwide. And we now have a framework theory of the terrestrial planets into which these phenomena neatly fit and for which there is telling evidence. For Comet Venus, there is also newly interpreted, compelling iconographic and linguistic evidence. The names of both Athena (A Fena, the Phoenician) and Poseidon (Bos eidon, the Bull of Heaven), for instance, referred to the double-tailed Venus.
So with new-found confidence that the Ancients and Velikovsky were right about Venus, we can ask how can we use this to decipher aspects of the culture of the Ancient Near East and of the background of Islam.
Tags: Ancient Near East, Ashur, Astarte, Ishtar, Islam, Kaaba, Mohammed, planetary science, Velikovsky, venus
 There’s no shortage of candidates for the cause of the mass extinctions of prehistory. But experts have found flaws in every one.
There’s no shortage of candidates for the cause of the mass extinctions of prehistory. But experts have found flaws in every one.
Asteroid impact at Chicxulub, Yucatan clearly played a role in the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction that wiped out the non-flying dinosaurs 66,000,000 years ago, though scientists point to the serious disruptions that had begun hundreds of thousands of years before with the basalt flows of the Deccan Traps. Giant basalt lava flows that poisoned the atmosphere and oceans played a role in four or perhaps all five major extinctions. But other enormous basalt flows have not caused extinctions, nor did they cause the tsunamis associated with various extinctions. Researchers have suggested many other mechanisms, but there’s no consensus at all.
Lurking in the background, however, is a quite plausible cause, one that would have possessed the power to set off the volcanic activity, air pollution, mass wasting, sea level shifts, loss of oxygen in oceans, climate changes, and other phenomena associated with the extinctions.
The Martian Theory
Tags: catastrophe, Chicxulub, climate change, Deccan Traps, dinosaurs, earth science, extinctions, geology, great mass extinctions, Mars, paleontology, planetary science, prehistory, tsunamis, Valles Marineris
 Based on his interpretation of ancient sources, Immanuel Velikovsky argued famously that Venus had emerged from Jupiter as a comet; interacted with the Earth and Mars in the second and first millennia BC, causing the Bronze Age catastrophes; and then finally settled into a nearly circular orbit of the Sun.
Based on his interpretation of ancient sources, Immanuel Velikovsky argued famously that Venus had emerged from Jupiter as a comet; interacted with the Earth and Mars in the second and first millennia BC, causing the Bronze Age catastrophes; and then finally settled into a nearly circular orbit of the Sun.

 Once a leading theory of the origin of the Earth-Moon system, the Capture Theory is simple and intuitively plausible. The numerous instances of moons with retrograde orbits show that capture is fairly common. The lunar orbit’s three moments of inertia are consistent with a past very eccentric orbit, suggestive of capture
Once a leading theory of the origin of the Earth-Moon system, the Capture Theory is simple and intuitively plausible. The numerous instances of moons with retrograde orbits show that capture is fairly common. The lunar orbit’s three moments of inertia are consistent with a past very eccentric orbit, suggestive of capture
 originally formed a single planet outside the orbit of Jupiter. Early in Solar System history, Jupiter’s powerful gravitational field pulled this planet past the gas giant. As the planet neared Jupiter, tidal friction heated it to the melting point, and Jupiter tore Mars away from Earth, leaving the Pacific Basin and an array of evidence on both planets. Earth and Mars then sped off into the inner solar system.
originally formed a single planet outside the orbit of Jupiter. Early in Solar System history, Jupiter’s powerful gravitational field pulled this planet past the gas giant. As the planet neared Jupiter, tidal friction heated it to the melting point, and Jupiter tore Mars away from Earth, leaving the Pacific Basin and an array of evidence on both planets. Earth and Mars then sped off into the inner solar system.



 If we can interpret certain ancient myths correctly, they could lead us to more accurate and penetrating views of the history of the Earth and the solar system. They might teach us about the forces at work and explain anomalies bequeathed to us by a long-hidden past. But how can we interpret these myths, the products of minds so far removed from ours? How do we know which interpretation is correct, if any? Are we doomed to speculate without ever achieving certainty?
If we can interpret certain ancient myths correctly, they could lead us to more accurate and penetrating views of the history of the Earth and the solar system. They might teach us about the forces at work and explain anomalies bequeathed to us by a long-hidden past. But how can we interpret these myths, the products of minds so far removed from ours? How do we know which interpretation is correct, if any? Are we doomed to speculate without ever achieving certainty? There’s no shortage of candidates for the cause of the mass extinctions of prehistory. But experts have found flaws in every one.
There’s no shortage of candidates for the cause of the mass extinctions of prehistory. But experts have found flaws in every one.